Table of Contents
In this guide, we’ll dive into the most common leadership styles, breaking down their advantages and drawbacks in a clear and straightforward manner. You’ll get a practical and comprehensive overview that helps you understand not just what these styles are, but also how they work in real-world situations. Whether you’re a current leader looking to refine your approach, or you’re just stepping into a leadership role, this guide will provide you with valuable insights to help you navigate the complexities of leadership effectively.
It’s important to clarify that choosing a leadership style is neither a permanent nor an either-or decision. Most successful leaders have a knack for picking and combining different styles of leadership with good situational awareness.
Preface: Situational Leadership And The Emotional Intelligence Model
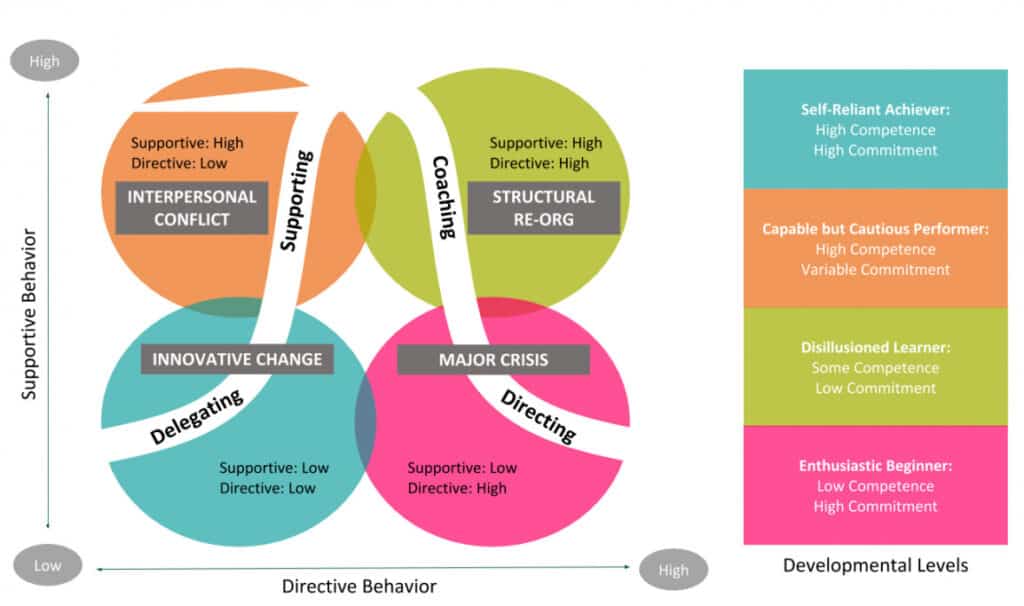
Introduction to Situational Leadership
Situational leadership is a flexible and adaptive leadership style that proposes the need for leaders to adjust their approach based on the situation and the maturity level of their team members. Developed by Paul Hersey and Ken Blanchard, this model emphasizes that there is no single “best” style of leadership. Instead, it hinges on the leader’s ability to assess the competence and commitment of their team members and adapt their style accordingly. Situational leadership is divided into four distinct quadrants: Delegating, Supporting, Coaching, and Directing. Each of these styles is suited to different levels of team member readiness and maturity.
1. Directing (High Directive, Low Supportive Behavior)
In the Directing quadrant, the leader provides specific instructions and closely supervises task accomplishment. This approach is best suited for team members who are enthusiastic but lack the necessary skills for the task at hand. They need clear guidance and direction on how to perform their tasks. The leader’s role here is more of a traditional boss – setting goals, establishing timelines, and showing how to achieve the tasks. This style is characterized by a high level of directive behavior and a low level of supportive behavior.
2. Coaching (High Directive, High Supportive Behavior)
Coaching is necessary when team members are more capable but still require guidance and encouragement. In this quadrant, the leader still provides direction, but there’s also a lot of two-way communication. The leader helps build confidence and motivation, but decision-making becomes more collaborative. This style involves a high degree of both directive and supportive behaviors, recognizing that while the team member is developing, they still need guidance and encouragement.
3. Supporting (Low Directive, High Supportive Behavior)
Supporting leaders step back and facilitate decision-making. This style is used when team members have the skills they need but may lack confidence or motivation. The leader’s role is to listen, provide support, and encourage initiative. They facilitate problem-solving and decision-making but don’t directly lead tasks. This quadrant involves a low level of directive behavior and a high level of supportive behavior.
4. Delegating (Low Directive, Low Supportive Behavior)
In the Delegating quadrant, the leader takes a hands-off approach. This style is suitable for team members who are both capable and confident in their ability to handle tasks independently. The leader delegates tasks and provides little supervision or support, trusting the team members to take ownership and solve problems on their own. Here, both directive and supportive behaviors are low because the team member has both the competence and confidence to handle tasks independently.
Conclusion: The Versatility of Situational Leadership
Situational leadership is a highly versatile approach that recognizes the dynamic nature of leadership in practice. By understanding and adeptly applying these four styles – Directing, Coaching, Supporting, and Delegating – leaders can effectively respond to their team’s needs and promote a more productive, efficient, and engaged working environment. This adaptability not only enhances team performance but also contributes to individual team member growth, making situational leadership a powerful tool in the arsenal of any effective leader.
To understand more about motivating people, read my relevant post which details two models you can apply right away.
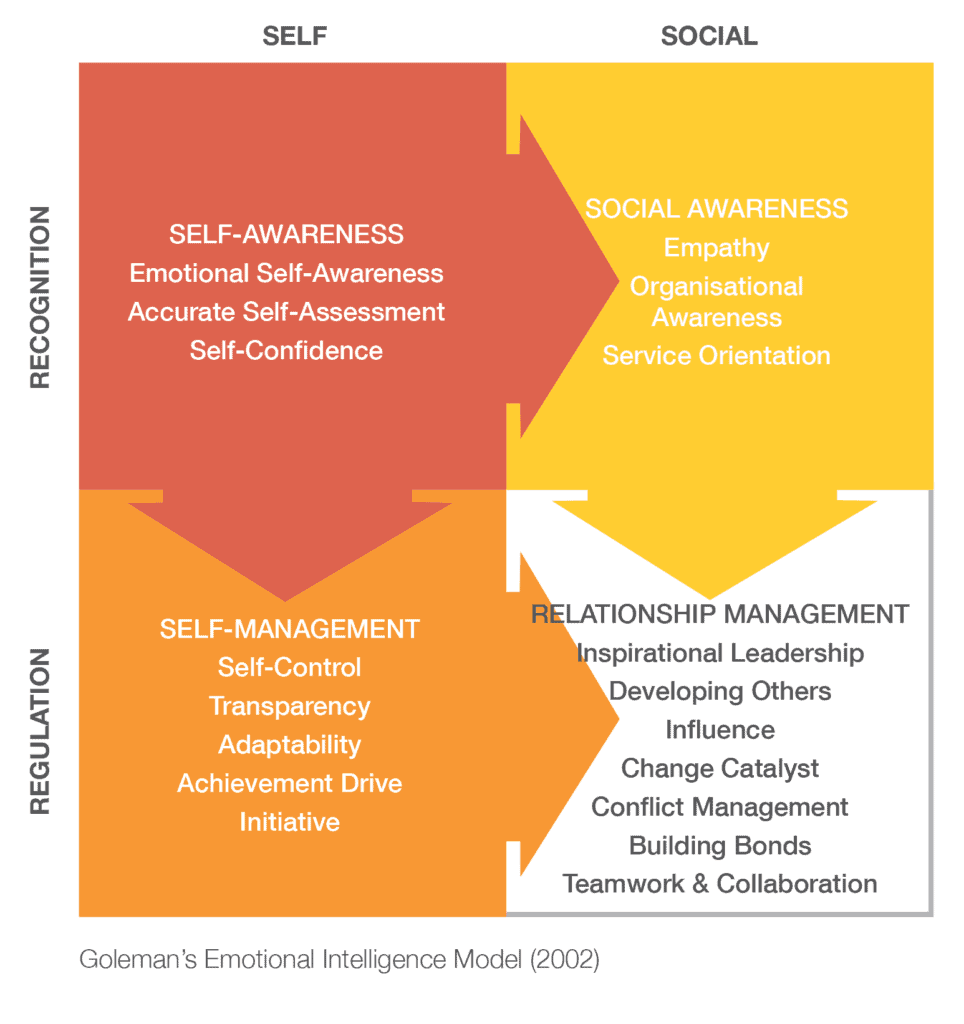
Daniel Goleman’s Emotional Intelligence (EI) Model is pivotal in understanding how emotional competencies can enhance personal and professional interactions. While Goleman originally identified five key components of EI, his model can also be viewed through a framework of four interrelated aspects: Self-Awareness, Social Awareness, Self-Management, and Relationship Management. These aspects are critical in developing one’s emotional intelligence and play a significant role in effective leadership and personal growth.
1. Self-Awareness
Self-awareness is the cornerstone of emotional intelligence. It involves being conscious of your own emotions, recognizing their impact, and understanding how they affect your thoughts and behavior. This aspect also includes an awareness of your strengths and weaknesses, which is essential for personal development.
- Leaders with high self-awareness are able to accurately assess their own emotional state and how it influences their interactions with others. This awareness allows them to make more informed decisions, manage stress effectively, and maintain a level-headed approach in various situations.
2. Social Awareness
Social awareness refers to the ability to understand and empathize with others. This involves being attuned to others’ emotions, needs, and concerns, as well as picking up on emotional cues in social interactions. It extends to understanding and navigating social networks and organizational dynamics.
- In a leadership context, social awareness is crucial for building rapport with team members, understanding team dynamics, and responding appropriately to the emotional needs of others. It helps leaders in fostering a supportive and inclusive work environment.
3. Self-Management
Self-management, or self-regulation, is about controlling and regulating your own emotions in response to different situations. This aspect involves managing impulsive feelings and behaviors, adapting to changing circumstances, and dealing with challenges constructively.
- Leaders who excel in self-management can maintain control in stressful situations, adapt to change with a positive attitude, and handle conflict diplomatically. This ability to remain composed and focused under pressure is essential for effective leadership.
4. Relationship Management
Relationship management involves using an understanding of your own emotions and those of others to manage interactions successfully. This aspect is about developing and maintaining good relationships, inspiring and influencing others, providing clear communication, and managing conflict.
- Leaders with strong skills in relationship management are able to build strong, collaborative teams, effectively manage change, resolve conflicts, and lead with a vision that motivates others. This aspect is key to building a cohesive team and fostering a positive workplace culture.
Conclusion: Integrating the Aspects of Emotional Intelligence for Personal and Professional Growth
Understanding and developing these four aspects of emotional intelligence is crucial for anyone looking to enhance their leadership capabilities and interpersonal skills. By cultivating self-awareness, social awareness, self-management, and relationship management, individuals can navigate the complexities of personal and professional relationships more effectively, lead with empathy and understanding, and create a positive impact in their organizations and communities. Embracing and integrating these aspects of emotional intelligence can lead to more meaningful interactions, better decision-making, and a more fulfilling personal and professional life.
1, The Autocratic Leadership Style
TL;DR
Let’s start with the most controversial one — the style we all love to hate. Many people dislike autocratic leadership because it can feel controlling and one-sided. In this style, the leader makes all the decisions without much input from others, which can make team members feel ignored and undervalued. This lack of teamwork and open discussion often leads to frustration and a negative view of the leadership style.
In some situations, though, autocratic leadership can be very effective. This style is useful when quick decisions are needed, like in emergencies or high-pressure scenarios. Because the leader makes all the decisions, it can lead to fast action and clear direction, which is crucial in urgent or critical situations. This approach can help avoid confusion and delays that might occur in a more democratic decision-making process.
The Essence of Autocratic Leadership: Swift Decisions in Critical Times
Autocratic leadership, often characterized by its straightforward yet powerful motto “Follow this plan,” stands as a beacon of decisiveness and authority in situations that demand swift action. This leadership style is defined by the leader making quick, firm decisions, often unilaterally, and directing team members with clear, specific instructions. The primary strength of autocratic leadership lies in its ability to provide immediate direction and clarity in scenarios where hesitation or ambiguity could lead to detrimental outcomes. In this style, the leader acts as the sole decision-maker, effectively cutting through potential indecision and debate that could slow down the response time.
The utility of autocratic leadership becomes particularly evident in crisis or environments where rapid decisions are crucial. During emergencies, the luxury of time for collaborative decision-making is often unavailable, and the need for prompt, decisive action takes precedence. Autocratic leaders excel in these scenarios by taking charge and providing unambiguous directives, thereby ensuring a coordinated and timely response. The key here is the leader’s ability to quickly assess the situation, identify the most effective course of action, and communicate it effectively to their team. This approach minimizes confusion and maximizes efficiency, which is vital in high-stakes or time-sensitive situations.
Autocratic Leadership in Practice: Navigating Emergencies with Precision and Authority
Consider the context of handling an emergency, such as a natural disaster response or a critical incident in a high-risk industry. In these circumstances, the autocratic leadership style is not just beneficial; it’s often necessary. The leader’s role transforms into that of a commander who must make rapid decisions based on the available information and guide their team with firm directives. This leadership style ensures that there is a clear chain of command and that actions are taken swiftly to mitigate risks and manage the situation effectively.
Historical and contemporary examples abound where autocratic leadership has proven invaluable during crises. Leaders in these scenarios have typically been praised for their ability to make tough decisions quickly, and their assertive approach in directing teams under pressure. However, it’s crucial to acknowledge that while autocratic leadership is highly effective in emergencies, its application in regular, day-to-day operations may not yield the same positive results. This style can be perceived as overbearing or stifling in environments that benefit more from collaboration and shared decision-making. Therefore, the true art of autocratic leadership lies in knowing when to employ this approach and balancing it with other styles as the situation evolves. This ability to adapt one’s leadership style to the demands of the moment is what distinguishes truly great leaders.
The Double-Edged Sword of Autocratic Leadership: Potential Pitfalls and Risks
This style comes with notable downsides that can impact both the team and the organization negatively if not managed carefully. One of the most significant risks associated with autocratic leadership is the potential for decreased team morale and engagement. When decisions are consistently made unilaterally, team members may feel undervalued and disenfranchised, leading to a sense of disconnection from the organization’s goals and objectives. This lack of involvement in the decision-making process can stifle creativity and innovation, as team members may be less inclined to offer ideas and insights if they believe their contributions will not be considered.
Another critical concern is the risk of burnout and high turnover. Autocratic leaders often maintain high standards and exert significant control over workflows and processes. While this can lead to efficient decision-making in the short term, it can also create a stressful work environment. Team members may feel constantly under pressure to perform to exacting standards, without the autonomy to make decisions or contribute meaningfully to the direction of their work. This can lead to burnout, dissatisfaction, and ultimately, a higher turnover rate, as employees seek more collaborative and empowering work environments.
If you want to read more about the causes of workplace burnout, I have the perfect article for you.
The Limitations of Autocratic Leadership: A Barrier to Long-Term Success
In addition to affecting team morale and turnover, autocratic leadership can also hinder the development of future leaders within the organization. By centralizing decision-making power, autocratic leaders often fail to provide their team members with opportunities to develop critical leadership skills such as strategic thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making. This lack of development can create a leadership vacuum within the organization, making it challenging to promote from within when leadership positions become available.
Furthermore, autocratic leadership can lead to a lack of diversity in thought and perspective. When decisions are made by a single individual, there’s a risk of creating a homogenous approach that lacks the innovation and creativity that come from collaborative brainstorming and diverse viewpoints. This can be particularly detrimental in dynamic industries where adaptability and innovation are key to staying competitive.
In conclusion, while autocratic leadership can be a valuable tool in specific contexts, such as during emergencies or times of crisis, it’s crucial for leaders to recognize its limitations. Balancing this style with more collaborative approaches can help mitigate the risks associated with autocratic leadership, ensuring that the organization can benefit from decisiveness and direction without sacrificing team morale, innovation, and long-term success.
2, The Democratic Leadership Style
TL;DR
Democratic leadership, with the motto “What do you think?” is highly valued in environments where collaboration is key. This style focuses on including everyone’s input, which is great for team-oriented settings. An example of where this works well is when deciding on the direction of a team project. In democratic leadership, everyone has a voice in the decision-making process, leading to more diverse ideas and a stronger sense of team unity. This approach encourages open communication and shared responsibility, making it a popular choice for teams looking to work together effectively.
While democratic leadership is great for fostering collaboration and inclusivity, it’s not always the best approach in every situation. One of its main drawbacks is that it can be time-consuming. When many voices and opinions are involved, reaching a consensus can take longer, which might not be ideal in urgent or time-sensitive scenarios. Additionally, in situations where team members lack the expertise or information needed to make informed decisions, this leadership style can lead to less effective outcomes. Too much input can also create confusion and conflict, making it hard to arrive at a clear, unified decision. Therefore, in fast-paced, high-stakes, or highly specialized environments, relying solely on democratic leadership might not be the most effective strategy.
Embracing the Democratic Leadership Style: Fostering Inclusivity and Team Engagement
Democratic leadership, often hailed as one of the most effective styles in fostering team collaboration and inclusivity, thrives on valuing each team member’s input. At the heart of this approach is the belief that good ideas can come from anywhere, and that involving team members in the decision-making process leads to more innovative and effective outcomes. This style is particularly beneficial in settings where team cohesion and collective brainstorming are vital, such as in creative industries, research teams, and project-based work environments. By soliciting and incorporating diverse perspectives, democratic leaders can harness a wide range of insights, leading to well-rounded and thoroughly considered decisions.
One of the key strengths of democratic leadership is its impact on team morale and engagement. When team members feel their voices are heard and their opinions valued, it fosters a sense of ownership and commitment to the team’s goals. This inclusive approach can also enhance the quality of decision-making, as it draws upon the collective knowledge and experience of the entire team. In scenarios like setting the direction for a team project, democratic leadership proves invaluable in ensuring that all aspects of the project are considered and that the team is collectively invested in the chosen path forward.
The Challenges and Limitations of Democratic Leadership
However, democratic leadership is not without its challenges. The most significant limitation of this style is its potential inefficiency in decision-making. The process of seeking input from all team members and reaching a consensus can be time-consuming. In situations where quick decisions are necessary, such as in crisis management or fast-paced market environments, the democratic approach may lead to delays and missed opportunities. This can be particularly problematic when swift action is needed to respond to external challenges or capitalize on fleeting market opportunities.
Another potential downside is the risk of decision paralysis or ‘analysis paralysis,’ where the abundance of opinions and perspectives leads to an inability to make a decision at all. This can occur in teams where there are conflicting viewpoints or when no clear consensus emerges. Additionally, in teams where members lack the necessary expertise or knowledge to contribute effectively to the decision-making process, the quality of decisions can be compromised. This highlights the importance of balancing democratic principles with a pragmatic understanding of the team’s capabilities and the context in which decisions are being made.
Striking the Right Balance: When to Use Democratic Leadership
The effectiveness of democratic leadership largely depends on the context in which it is applied. It works best in collaborative environments where team input is crucial for success and where there is enough time to allow for a thorough discussion and consensus-building process. Examples include strategic planning, product development, and policy formulation, where the collective wisdom of the team can lead to more innovative and effective solutions.
However, leaders should be mindful of the limitations of this style and be prepared to adapt their approach in situations where it may not be the most effective. In emergencies, time-critical decisions, or highly specialized fields where expert knowledge is paramount, a more directive or specialized leadership approach might be more appropriate.
In conclusion, democratic leadership is a powerful tool for fostering collaboration, innovation, and team commitment. However, its effectiveness is contingent on the leader’s ability to recognize when this inclusive approach will be most beneficial and when it might be necessary to adopt a different style to meet the demands of the situation. By understanding and navigating these nuances, leaders can maximize the benefits of democratic leadership while avoiding its potential pitfalls.
3, The Adaptive Leadership Style
TL;DR
Adaptive leadership is all about being flexible and ready to change when things around you are shifting quickly. It’s especially useful in situations like when a company needs to change direction because of new market trends or during a big company shake-up. The key idea of this leadership style is asking, “How can we adjust?” This means constantly looking for the best way to respond to new challenges and changes.
While adaptive leadership is valuable in fast-changing environments, it’s not without its drawbacks. This style often involves constant change, which can be unsettling for teams who prefer stability and clear, long-term directions. Constantly adapting to new situations can also lead to a lack of consistent strategy, making it hard for teams to focus on long-term goals. This intro aims to explore these and other challenges associated with adaptive leadership, offering insights into its potential limitations.
Adaptive Leadership in Action
In the business world, adaptive leaders are always keeping an eye on things like what competitors are doing, new technologies, and what customers want. They’re ready to change their plans if it means doing better in the market. For example, when shopping moved from stores to online, adaptive leaders were the ones who saw the trend and shifted their business to fit it.
A big part of being an adaptive leader is making sure your team is also ready to change and try new things. It’s about encouraging everyone to be open to new ideas and not to be afraid of failing every so often. This is really important in situations like when a company is reorganizing because it helps everyone adapt to new ways of working more easily.
The Ups and Downs of Adaptive Leadership
Being an adaptive leader isn’t always easy. It means making decisions even when you’re not sure about everything, and being ready to change those decisions when new information comes in. But, if you can do it well, it can make your organization stronger and more able to handle whatever comes its way.
In short, adaptive leadership is key in today’s world where things are always changing. It helps leaders and their teams to stay ahead of the curve, be innovative, and successfully navigate through changes and new challenges.
4, The Coaching Leadership Style
TL;DR
In the diverse spectrum of leadership styles, coaching leadership stands out for its focus on developing people’s skills and preparing them for future challenges. This approach is less about directing and more about guiding team members towards realizing their full potential. Ideal for fostering personal growth and upskilling teams, coaching leadership is particularly effective in environments where continuous learning and development are key to success.
One of the primary drawbacks of this style is the significant time and effort required from the leader. Coaching demands a substantial investment in one-on-one interactions and personalized development plans, which can be challenging to sustain, especially in larger teams or fast-paced environments. Another potential issue is the reliance on the willingness and ability of team members to engage in the coaching process. Not all individuals are receptive to or comfortable with the introspective and participative nature of coaching. Some may prefer more directive or hands-off leadership styles. Additionally, the coaching style may not always align with immediate business needs. In situations where quick decision-making and rapid action are required, the deliberative and developmental approach of coaching can be seen as too slow or impractical. Balancing the long-term benefits of coaching with the immediate demands of the business can be a challenging task for leaders.
The Core of Coaching Leadership: Nurturing Talent and Encouraging Growth
The essence of coaching leadership lies in its personalized approach to team development. Leaders who adopt this style act as mentors to their team members, investing time and effort in understanding their unique strengths, weaknesses, and aspirations. This style is characterized by one-on-one interactions, regular feedback, and a deep commitment to the professional growth of each team member. The goal is not just to enhance the current performance, but to build skills and capabilities for future roles and challenges.
Coaching leaders focus on asking insightful questions rather than providing direct answers. This Socratic method encourages team members to think critically, solve problems independently, and develop a growth mindset. By fostering an environment of open communication and trust, coaching leaders empower their teams to take ownership of their learning and career development. This approach is especially beneficial in dynamic industries where adaptability and continuous learning are crucial.
Practical Applications: Upskilling Teams for Future Success
In practice, coaching leadership goes beyond just managing day-to-day tasks. It involves setting up developmental plans, identifying learning opportunities, and guiding team members through challenges. For instance, in a project setting, a coaching leader might delegate a challenging task to a team member, not just to get the job done, but more importantly, to develop that individual’s skills and confidence.
This style is particularly effective in scenarios where teams need to adapt to new technologies or methodologies. A coaching leader can guide their team through the learning curve, ensuring that each member is equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge. This not only enhances the team’s capabilities in the short term but also prepares the organization for future challenges.
Challenges and Considerations in Coaching Leadership
While the benefits of coaching leadership are numerous, there are challenges and considerations to keep in mind. This style requires a significant investment of time and effort from the leader, which might not be feasible in all types of organizations or situations. Additionally, the success of this approach depends heavily on the willingness and ability of team members to engage in self-reflection and personal development.
Moreover, in high-pressure situations where quick decisions are required, the deliberative nature of coaching might not be the most efficient approach. Leaders may need to balance coaching with more directive styles to meet immediate business needs.
Conclusion: The Lasting Impact of Coaching Leadership
In conclusion, coaching leadership is a powerful tool for developing a skilled, adaptable, and motivated workforce. By focusing on personal growth and skill development, coaching leaders can build teams that are not only effective in their current roles but also prepared for future challenges. While it requires a significant commitment and the right organizational culture to be truly effective, the long-term benefits of a well-developed team are immeasurable. As businesses continue to evolve in an ever-changing landscape, the ability to coach and develop talent will remain a vital skill for effective leaders.
5, The Strategic Leadership Style
TL;DR
This leadership style is all about looking at the bigger picture and steering the team or organization towards a future vision. Ideal for guiding companies through periods of growth or significant change, strategic leadership is encapsulated by the motto, “Here’s my vision.” It’s about setting a clear, ambitious direction for the future and meticulously planning how to get there.
However, strategic leadership is not without its challenges. One of the key difficulties is maintaining the balance between long-term vision and short-term operational needs. There’s also the risk of being so focused on the future that immediate issues or opportunities are overlooked. Moreover, in a rapidly changing business environment, sticking rigidly to a long-term plan can sometimes be counterproductive. Strategic leaders must be flexible enough to adapt their vision in response to new information or changes in the market.
The Essence of Strategic Leadership: Balancing Today’s Actions with Tomorrow’s Goals
At the heart of strategic leadership is the ability to develop and communicate a compelling vision, such as a 5-year business plan or a long-term technical vision. This requires not just foresight and imagination but also a deep understanding of the current market trends, internal strengths and weaknesses, and potential opportunities and threats. A strategic leader is adept at analyzing various factors that could affect the organization’s future and crafting a roadmap that guides its journey towards success.
A key aspect of this leadership style is the focus on long-term success rather than short-term gains. This involves making decisions and setting priorities that may not pay off immediately, but are crucial for future growth and stability. It’s about understanding the importance of investing in resources, people, and innovations that will drive the organization forward in the years to come.
Implementing Strategic Leadership: Guiding Teams with Clarity and Purpose
In practice, strategic leadership involves a lot more than just setting goals. It’s about breaking down the vision into achievable objectives and creating a culture where everyone is aligned with and working towards these goals. For instance, when developing a 5-year business plan, a strategic leader would involve key team members in the planning process, ensuring that their insights and expertise shape the final plan. This collaborative approach not only enriches the plan but also fosters a sense of ownership and commitment among team members.
Furthermore, strategic leaders are skilled at navigating change and uncertainty. They are not deterred by short-term setbacks and remain focused on the end goal. They also play a crucial role in inspiring and motivating their teams, especially during challenging times, by reminding them of the bigger picture and the impact of their work.
Conclusion: The Enduring Impact of Strategic Leadership
In conclusion, strategic leadership is essential for any organization or team aiming to achieve sustained success and growth. By aligning actions with a well-defined long-term vision, strategic leaders can guide their teams through growth and change with confidence and clarity. While this leadership style comes with its own set of challenges, its importance in today’s dynamic business landscape cannot be overstated. Effective strategic leadership not only shapes the future of organizations but also inspires and empowers individuals to contribute to a shared, ambitious goal.
6, The Inspirational Leadership Style
TL;DR
Inspirational leadership is a dynamic and impactful style that revolves around motivating and uplifting teams through a compelling vision and passion. Perfectly encapsulated by the motto “Let’s aim higher,” this approach is about igniting enthusiasm and commitment among team members, rallying them around a common goal or vision. It’s particularly effective in scenarios like introducing a new company direction or a groundbreaking technology vision, where the ability to inspire and unite a team is crucial for success.
However, like any leadership style, inspirational leadership has its challenges. The balance between inspiring and remaining grounded in reality is delicate. There is a risk of over-promising or creating expectations that may not be entirely realistic. Inspirational leaders must ensure that their vision is achievable and backed by a solid plan. Another challenge is ensuring that the drive to inspire does not overshadow the need for clear communication and practical strategies. The team’s enthusiasm needs to be channeled into actionable steps and sustained efforts towards the goal.
The Essence of Inspirational Leadership: Fueling Progress with Passion
Inspirational leaders are characterized by their ability to articulate a clear and exciting vision for the future. They are not just managers or supervisors; they are visionaries who see beyond the day-to-day tasks and focus on the bigger picture. Their strength lies in their ability to communicate this vision in a way that is not only understandable but also compelling and motivating for their team. This involves using powerful storytelling, evocative language, and personal charisma to connect with team members on an emotional level.
The true power of inspirational leadership is its ability to create a sense of purpose and belonging among team members. When people feel part of something bigger than themselves, they are more likely to be engaged, committed, and willing to go the extra mile. This is especially important in times of change or uncertainty, such as during a company rebranding or a shift in strategic direction, where the morale and buy-in of the team are critical.
In Practice: Rallying Teams Around New Visions
In practice, inspirational leadership can take many forms, but it often involves leading by example, showing genuine enthusiasm and belief in the vision, and recognizing and celebrating the contributions of team members. For example, when introducing a new technology vision, an inspirational leader would not only explain the technical aspects but also paint a vivid picture of how this technology could revolutionize the industry and positively impact the team and the broader world.
Inspirational leaders also create environments that foster creativity, innovation, and collaboration. They encourage their teams to think outside the box, take risks, and embrace new ideas. This is particularly effective in creative industries or startups, where agility and innovation are key drivers of success.
7, The Laissez-Faire Leadership Style
TL;DR
Laissez-faire leadership, characterized by its hands-off approach and the motto “You’ve got this,” stands as a unique and effective style in environments where team independence is key. Ideal for skilled and self-driven teams, this leadership approach is about entrusting team members with the freedom and autonomy to manage their tasks and make decisions. It’s particularly effective when managing a group of experienced experts, where the leader’s role shifts from being a director to more of a facilitator.
However, laissez-faire leadership is not without its challenges. It’s crucial that this style is applied in the right context and with the right team. It works best with highly skilled and motivated teams who require little oversight. In situations where team members lack experience, confidence, or motivation, this style can lead to confusion, lack of direction, and poor performance. Moreover, there is a risk of leaders becoming too detached, which can result in a lack of accountability and cohesion within the team. Leaders must find the right balance between giving autonomy and remaining engaged, ensuring that the team’s work aligns with the organization’s broader objectives.
The Essence of Laissez-Faire Leadership: Trust and Empowerment
At the core of laissez-faire leadership is a deep trust in the team’s abilities and judgment. Leaders who adopt this style are confident in their team’s expertise and are comfortable stepping back to let team members take the lead. This approach is not about abdicating responsibility, but about empowering team members to take ownership of their work. By doing so, it fosters a sense of responsibility, enhances motivation, and can lead to more innovative and creative solutions, as team members feel free to experiment and explore new ideas. Read my two cents on “Stop Changing, Start Experimenting”.
Laissez-faire leadership is particularly effective in fields where specialized knowledge or expertise is required, such as in research teams, creative industries, or high-tech sectors. In these environments, the leader’s role is to provide the resources and support needed, and then trust the team to execute effectively. This empowerment can lead to high levels of job satisfaction and a strong sense of team cohesion, as members feel valued and trusted.
Practical Application: Leading Skilled, Self-driven Teams
In practice, laissez-faire leadership requires a careful balance. It’s important that leaders remain accessible and supportive, providing guidance and assistance when needed, but without micromanaging. For instance, when overseeing a group of experienced professionals, a laissez-faire leader might set the overall goals and parameters for a project and then step back, allowing the team to determine the best way to achieve these objectives.
Effective communication is also key in this leadership style. Leaders need to ensure that team members understand the overall vision and goals, and then give them the latitude to work independently towards these aims. Regular check-ins and feedback sessions can help maintain alignment and provide opportunities for support and course correction if necessary.
Conclusion: Maximizing the Potential of Laissez-Faire Leadership
In conclusion, laissez-faire leadership is a powerful approach in the right circumstances, particularly with teams of experienced and self-driven professionals. By empowering team members with independence and trust, leaders can foster an environment of innovation, satisfaction, and high performance. While this style requires careful application and a keen understanding of the team’s dynamics, it can lead to impressive results when implemented effectively.
8, The Transformational Leadership Style
TL;DR
Transformational leadership is a powerful approach for driving significant change and innovation within organizations. With the motto “Let’s change the game,” this leadership style is especially relevant when guiding teams through innovative projects or executing new business strategies. It’s about inspiring and motivating team members to not only accept but embrace and drive change, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
However, transformational leadership comes with its set of challenges. One key consideration is balancing the drive for innovation with the realities of the organization’s current situation and constraints. Leaders must ensure that their ambitious visions are grounded in practicality and achievable within the resources and capabilities of the team. Another potential challenge is ensuring that the focus on big-picture change does not overlook the smaller, day-to-day operational aspects that are critical to the organization’s success. Transformational leaders need to maintain a holistic view, ensuring that while they drive change and innovation, the fundamental operations and processes are not neglected.
The Core of Transformational Leadership: Inspiring Change and Fostering Innovation
The essence of transformational leadership lies in its ability to energize and inspire team members. Transformational leaders are visionaries who can paint a compelling picture of the future and rally their teams around it. They are adept at connecting individual goals with the larger mission of the organization, making each team member feel integral to the overall success. This type of leadership goes beyond managing day-to-day operations; it’s about fostering a culture of continuous improvement, creativity, and innovation.
Transformational leaders are also characterized by their ability to challenge the status quo and encourage out-of-the-box thinking. They are not afraid to take risks or to encourage their teams to do so. This approach is crucial when executing a new business strategy or leading an innovative project, as it requires a departure from conventional thinking and a willingness to explore new ideas and approaches.
Practical Application: Navigating New Strategies and Innovative Projects
In practice, transformational leadership can be seen in actions such as encouraging team members to think creatively about solving problems, promoting a collaborative environment where new ideas are valued, and providing the support and resources needed to turn these ideas into reality. For example, when executing a new business strategy, a transformational leader would not only outline the strategic vision but also actively engage with the team to brainstorm innovative approaches, overcome challenges, and achieve milestones.
This leadership style also involves recognizing and celebrating achievements, both big and small. This recognition helps to build momentum and sustain enthusiasm, keeping the team motivated and focused on the end goal. Moreover, transformational leaders are continually looking for ways to develop their team’s skills and competencies, providing opportunities for growth and development that align with the strategic direction of the organization.
Conclusion: The Impact of Transformational Leadership on Organizational Success
In conclusion, transformational leadership is an essential style for organizations looking to navigate through significant changes or embark on innovative projects. By inspiring, motivating, and guiding teams, transformational leaders can create an environment where change is not only possible but embraced as an opportunity for growth and improvement. While this approach requires careful balancing and a deep understanding of the team and organizational dynamics, its potential to drive significant positive change makes it a valuable tool in any leader’s repertoire.
9, The Transactional Leadership Style
TL;DR
Transactional leadership, encapsulated by the motto “Meet these goals,” is a pragmatic and goal-oriented approach that focuses on the relationship between leaders and their team members in terms of rewards and penalties. This leadership style is particularly effective in environments where clear, measurable outcomes are needed, such as meeting sales targets or achieving specific project milestones. It’s about setting clear expectations and then rewarding or penalizing team members based on their performance against these expectations.
However, transactional leadership has its limitations. One of the main criticisms of this style is that it can lead to a somewhat transactional (hence the name), even mechanical, work environment. The focus on rewards and penalties can overshadow other motivational factors such as personal growth, creativity, and intrinsic job satisfaction. Additionally, this leadership style may not be effective in environments where innovation and creativity are required. In such settings, the emphasis on structured rewards and penalties might stifle innovation and discourage team members from taking risks or thinking outside the box.
The Mechanics of Transactional Leadership: Performance-Based Management
At its core, transactional leadership operates on the principle of reward and punishment. Leaders who adopt this style are typically very clear about what needs to be achieved and what the rewards will be for meeting these objectives. They are also explicit about the consequences of failing to meet the set targets. This clarity can be highly motivating for team members who are driven by tangible outcomes and clear markers of success.
This leadership style is particularly effective in tasks that require a high level of oversight and control. For example, in sales environments where meeting targets is essential, transactional leaders can effectively motivate their teams by setting clear goals and linking these directly to reward such as bonuses, commissions, or promotions. Similarly, in project-based work, this approach can help keep team members focused and aligned with specific deadlines and quality standards.
Transactional Leadership in Practice: A Focus on Results
In practice, transactional leadership involves regular monitoring of performance, providing feedback, and ensuring that team members are held accountable for their results. Leaders in this style are often very hands-on in managing their teams, with a strong focus on operational efficiency and effectiveness. They are adept at identifying areas where performance can be improved and are quick to implement strategies to address these areas.
A key aspect of this leadership style is its straightforwardness – team members know exactly what is expected of them and what they need to do to succeed. This can lead to high levels of productivity and efficiency, as there is little ambiguity about what needs to be accomplished.
Conclusion: The Role of Transactional Leadership in Goal-Oriented Tasks
In conclusion, transactional leadership can be an effective tool for driving performance in goal-oriented tasks and environments where clear outcomes are key. Its focus on rewards and penalties can provide strong motivation and ensure that team members are aligned with specific objectives. However, leaders should be aware of the limitations of this style and consider complementing it with other approaches to foster a more holistic and motivating work environment.
10, The Servant Leadership Style
TL;DR
In the diverse landscape of leadership styles, servant leadership stands out for its focus on the welfare and development of team members. This approach, encapsulated by the motto “How can I support you?”, is centered on the leader taking a supportive role rather than a directive one. Servant leadership is particularly effective in creating nurturing and supportive work environments, where the focus is on the well-being and growth of the team members and the health of the team itself.
One potential pitfall is the risk of overextending in the quest to support team members, which can lead to burnout for the leader. Additionally, there is a balance to be struck between being supportive and maintaining the authority necessary to make tough decisions when required. Another consideration is ensuring that the focus on team well-being does not come at the expense of achieving organizational goals. While prioritizing team needs is crucial, servant leaders must also ensure that they are driving their teams towards achieving business objectives effectively.
The Heart of Servant Leadership: Empathy and Support
The core principle of servant leadership is the commitment to serving the needs of team members. Leaders who adopt this style prioritize the professional and personal growth of their employees above all else. This involves actively listening to team members, understanding their challenges and aspirations, and then doing whatever it takes to support them in achieving their goals. This could mean providing resources for professional development, offering emotional support during challenging times, or simply being available and approachable.
A servant leader is often seen more as a mentor or coach rather than a traditional boss. They lead by example, demonstrating humility, empathy, and a strong ethical foundation. This approach builds a strong sense of trust and respect within the team, as members feel valued and understood.
Read my post “Great Leaders Make People Feel Safe” for more on the topic.
Servant Leadership in Practice: Building a Culture of Support and Wellbeing
In practice, servant leadership manifests in various ways, depending on the needs of the team. For instance, in a scenario where a team is working on a high-pressure project, a servant leader might focus on ensuring that team members have a healthy work-life balance, providing support to alleviate stress and prevent burnout. In another scenario, the leader might focus on providing opportunities for skill development, recognizing that growth and learning are crucial for long-term career satisfaction.
A key aspect of servant leadership is the focus on building a strong, cohesive team culture. Servant leaders strive to create an environment where collaboration, open communication, and mutual respect are the norms. They understand that a supportive culture is fundamental to team performance and individual satisfaction.
Conclusion: The Transformative Impact of Servant Leadership
In conclusion, servant leadership offers a unique and effective approach to leadership, one that can lead to high levels of team satisfaction, strong cultures of trust, and ultimately, enhanced performance. By putting the needs of their team first, servant leaders can create a positive, supportive work environment where team members are motivated to contribute their best. While there are challenges to navigate, the benefits of a leadership style that genuinely prioritizes the well-being and development of team members can be far-reaching and transformative.
Closing Words
In wrapping up this comprehensive exploration of various leadership styles, it’s clear that each style has its unique strengths and challenges. From the directive nature of Autocratic leadership, valuable in crisis situations, to the inclusive approach of Democratic leadership, ideal for fostering collaboration and innovation, each style offers different tools for different situations. Similarly, Adaptive leadership’s flexibility is key in rapidly changing environments, while Coaching leadership’s focus on personal development is crucial for long-term team growth. Strategic, Inspirational, Transactional, and Servant leadership styles each bring distinct approaches to managing teams and achieving goals.
The essence of effective leadership lies in understanding these diverse styles and knowing when and how to apply them based on the situation at hand and the team’s needs. The ability to adapt and blend these styles is what truly defines a successful leader. Whether it’s steering through challenging times with Autocratic decisiveness, inspiring innovation with Transformational vision, or supporting team growth with Servant empathy, the art of leadership involves a dynamic and responsive approach.
Remember, leadership is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It’s a dynamic skill set that, when used judiciously and empathetically, can lead to remarkable outcomes for both leaders and their teams. As you navigate your leadership journey, keep these insights in mind, and aim to apply the most suitable style that resonates with your team’s needs and the objectives you seek to achieve. With this adaptive and informed approach, you’re well-equipped to lead effectively and make a positive impact in your professional environment.




